Using a password to secure your accounts is no longer sufficient in a world where cyber threats are on the rise and personal information is increasingly at risk. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) can help with that.
You’ve already used it if you’ve ever entered your password and got a code via SMS. However, what is 2FA, and why is it important?
Let’s simplify it so that it is easy to comprehend and even easier to put into practice.
What Is Authentication with Two Factors?
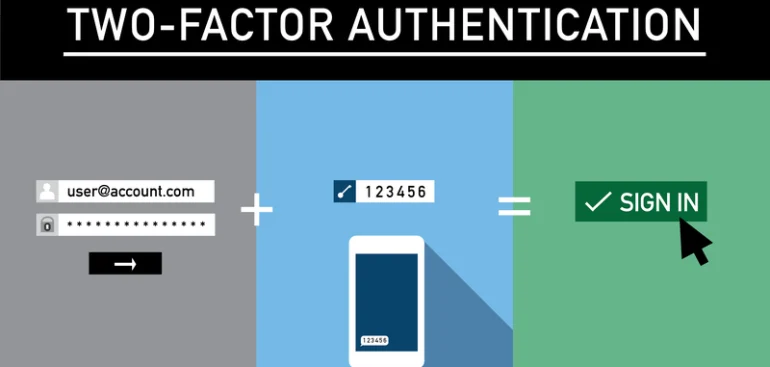
An additional security measure called two-factor authentication (2FA) is used to confirm that users attempting to access an online account are who they claim to be.
2FA demands a second form of identity in addition to a username and password.
Usually, these elements can be divided into three groups:
- Something you are familiar with, such as your password
- Something you own, such as a security key or your phone
- Something that identifies you, such as your facial ID or fingerprint
By requiring two of these to log in, 2FA makes it far more difficult for hackers to access your account.
What Makes 2FA Important?
1. Passwords by themselves are no longer secure.
Brute force assaults, phishing scams, and data breaches can compromise even strong passwords. If you don’t have 2FA activated, a hacker can access everything from your bank account to your emails once they have your password.
2. Additional Protection for Private Data
Even in the event that your password is compromised, 2FA makes sure that only you can access your data, including work files, social media accounts, and cloud storage.
3. It is simple and cost-free to use.
It only takes a few minutes to set up 2FA, which is supported by the majority of popular websites and apps. When it comes to digital safety, a little work goes a long way.
Typical 2FA Method Types
• Codes for SMS
A one-time code is sent to your mobile number. Easy, but not the safest—text messages can be intercepted by hackers.
• Apps for Authenticators
Time-based codes are generated on your phone by apps such as Authy, Microsoft Authenticator, and Google Authenticator. safer than SMS.
• Biometrics
Face recognition and fingerprint scanning are frequently seen in high-security apps and smartphones.
• Keys for security
Physical USB devices that connect to your computer to confirm your identity include YubiKey.
How to Turn on 2FA
The majority of platforms make activating 2FA simple:
- Navigate to the account settings.
- Look for “Login Options” or “Security.”
- “Two-Factor Authentication” should be selected.
- Select the mode of your choice (email, SMS, app, etc.).
- To link and validate your second factor, follow the instructions.
Concluding remarks
Digital identification is crucial in this day and age. Furthermore, safeguarding it is now required.
One of the simplest and most efficient methods to keep safe online is to use two-factor authentication. By turning on 2FA, you may feel secure knowing that your personal information is far more difficult to steal, whether you’re banking, buying, or just browsing social media.
Protect your accounts now rather than waiting for a breach. Prevention is always preferable to recovery in the field of cybersecurity.