Greetings from the future, where your refrigerator is aware of the food you’re running low on and your coffee maker communicates with your alarm clock. This is how the Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected gadgets, works to make houses more intelligent, effective, and customized than before.
By 2025, IoT is more than just a trendy term in technology; it’s becoming a commonplace aspect of everyday life. These are the best IoT gadgets that can completely change your living area if you’re considering remodeling your house.
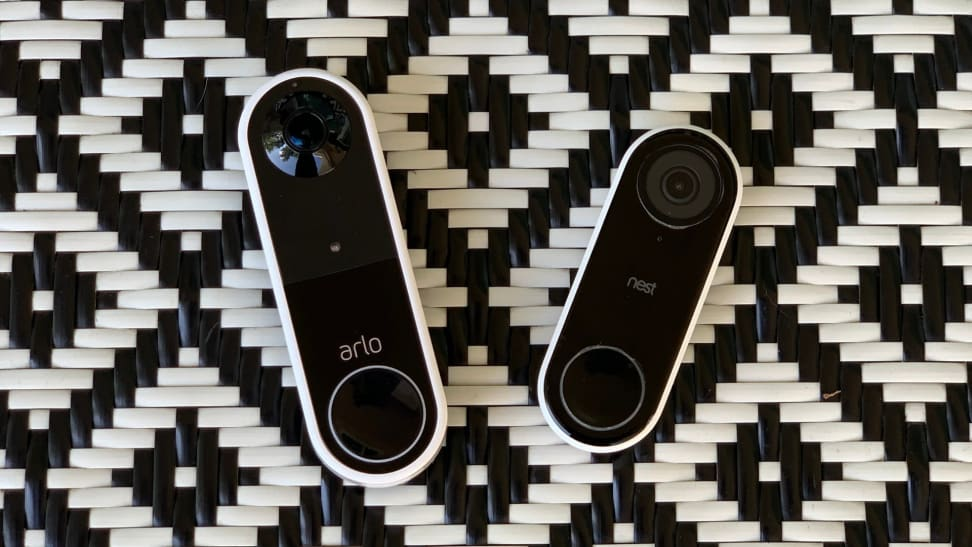
1. Smart doorbells, such as Nest Hello, Ring, and Arlo
Why you’ll adore it:
Using your phone, you can see who is at your door, have a remote conversation with them, and receive motion alerts. Ideal for improving peace of mind and security.
Important attributes:
- Streaming HD video
- Two-way audio
- Night vision and motion detection
- Cloud-based recording storage
2. Smart speakers, such as Apple HomePod, Google Nest Audio, and Amazon Echo
Why you’ll adore it:
You may use your voice to manage your calendar, play music, control your smart home, and even get weather reports.
Important attributes:
- Voice assistants, such as Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa
- Syncing multiple devices
- Functions of a home automation hub
- Smart schedules for music, locks, lighting, and other devices
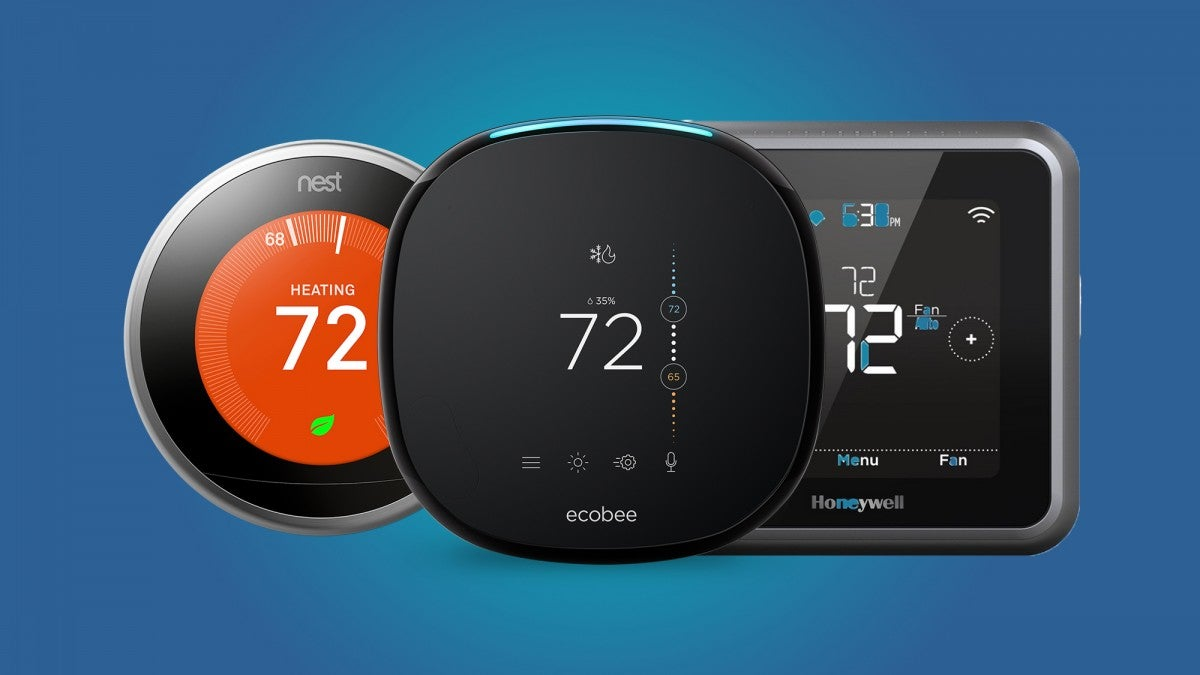
3. Smart thermostats, such as Honeywell Lyric, Ecobee, and Nest
Why you’ll adore it:
These gadgets automatically regulate the temperature based on your behavior, saving you money and energy.
Important attributes:
- Using an app, remotely control the temperature
- Astute scheduling
- Reports on energy use
- Compatibility with voice assistants
4. Smart lighting systems, such as Wyze, LIFX, and Philips Hue
Why you’ll adore it:
Color and brightness settings allow you to quickly change the mood of your house; you can control everything with voice commands or your phone.
Important attributes:
- Customization of color
- Voice control and an app
- Automation based on motion
- LED technology that uses less energy
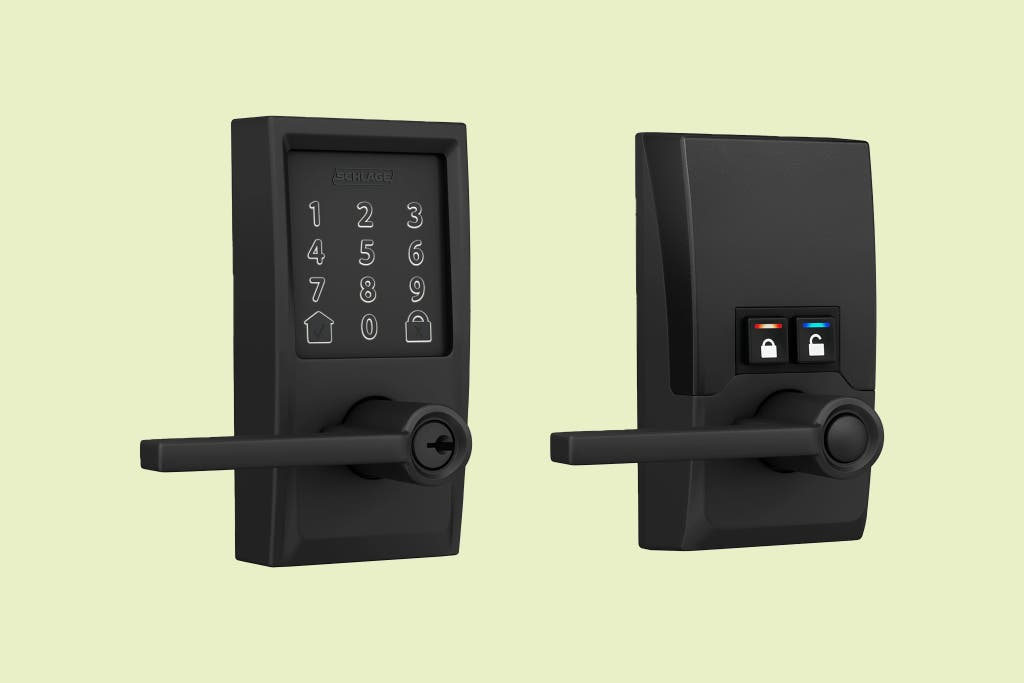
5. Smart locks, such as Yale, Schlage, and August
Why you’ll adore it:
Get security and lose the keys. Keyless entry, remote locking, and user-specific access codes are all made possible by smart locks.
Important attributes:
- Controlled locking and unlocking via a smartphone
- Adapt to your location to automatically lock and unlock
- Access codes for guests
- Connectivity to other smart home systems
6. Smart TVs (such as Sony Bravia, LG WebOS, and Samsung Smart Hub)
Why you’ll adore it:
They’re not just Netflix players. Your TV becomes your entertainment and control center thanks to intelligent integration and built-in voice assistants.
Important attributes:
- App compatibility
- Mirroring and screen casting
- Hands-free browsing and voice control
- Dashboard access for smart homes
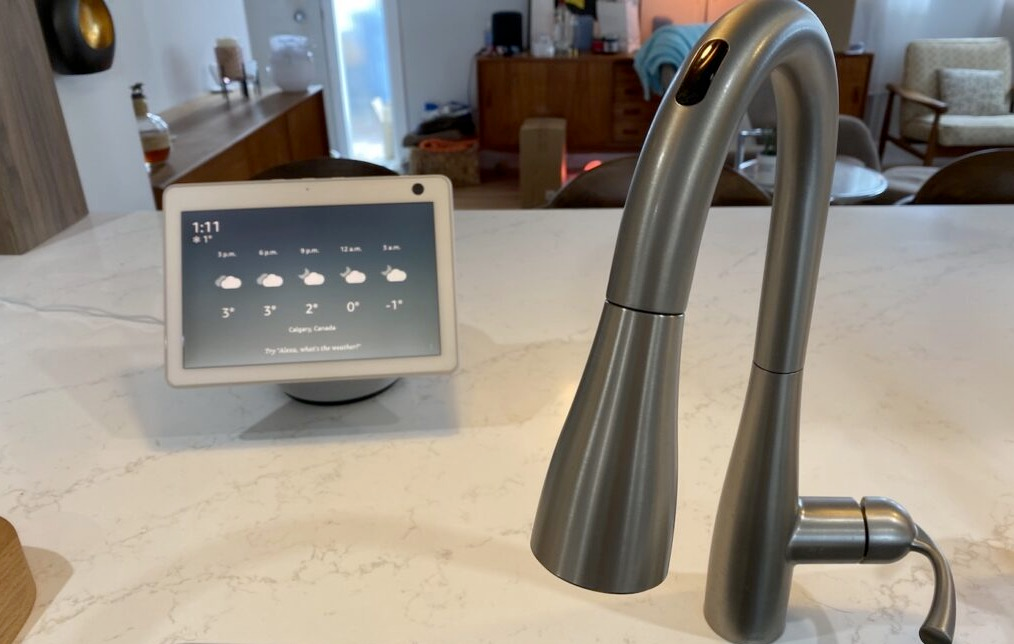
7. Smart faucets and showers (such as Kohler Konnect and Moen U by Moen)
Why you’ll adore it:
Before you enter, adjust the water’s temperature, pressure, and even the music.
Important attributes:
- Voice control and an app
- Family members’ pre-made profiles
- Water-saving technology
- Temperature safety parameters
8. Sleep trackers and smart mattresses (e.g., Withings Sleep, Eight Sleep)
Why you’ll adore it:
With mattresses that detect REM cycles and regulate temperature, you can get deeper sleep and gain insights into the quality of your sleep.
Important attributes:
- Analytics and tracking of sleep
- Control of temperature
- Intelligent alarms
- Apps that integrate health
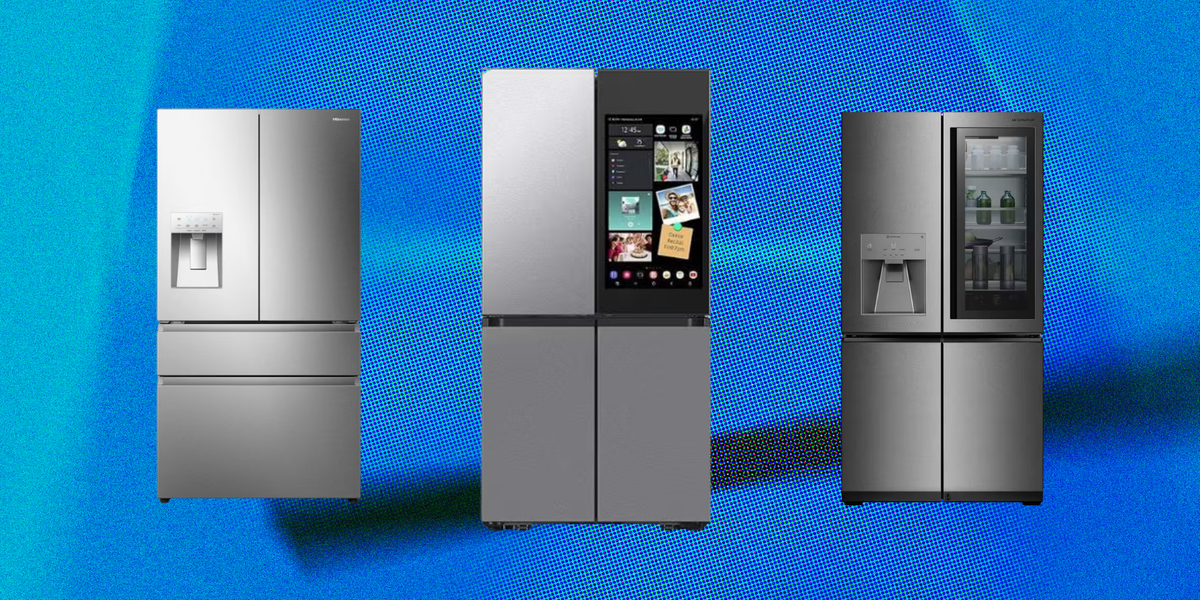
9. Smart appliances, such as the LG ThinQ washer and the Samsung Family Hub refrigerator
Why you’ll adore it:
These appliances tell you when maintenance is necessary, save time, and use less energy.
Important attributes:
- Monitoring the inventory of groceries
- Recipe recommendations
- Monitoring and remote control
- Alerts for maintenance
10. Robotic vacuums (such as the Eufy, Roborock, and iRobot Roomba)
Why you’ll adore it:
Don’t do any work to clean your flooring. Allow your vacuum to map out your house and avoid obstructions, and schedule or remotely start cleanings.
Important attributes:
- Astute mapping
- Control by voice
- Memory with multiple floors
- Recharging and auto-docking
Bonus: Connect Everything with a Smart Hub
Device unification, enabling smooth control, automation, and personalization, is facilitated by smart hubs such as Apple Home, Amazon Alexa, and Samsung SmartThings. Using a single tap or voice command, create scenes like “Good Morning” or “Movie Night.”
Concluding remarks
By 2025, homes will be smarter, more efficient, and customized to our lifestyles thanks to the Internet of Things revolution. Even while the convenience is amazing, don’t forget to put security first. Make sure your passwords are strong and one-of-a-kind, and update your devices frequently.
These top IoT gadgets are a great place to start, whether you’re building a completely connected home or just upgrading one item. The future is linked, not simply intelligent.