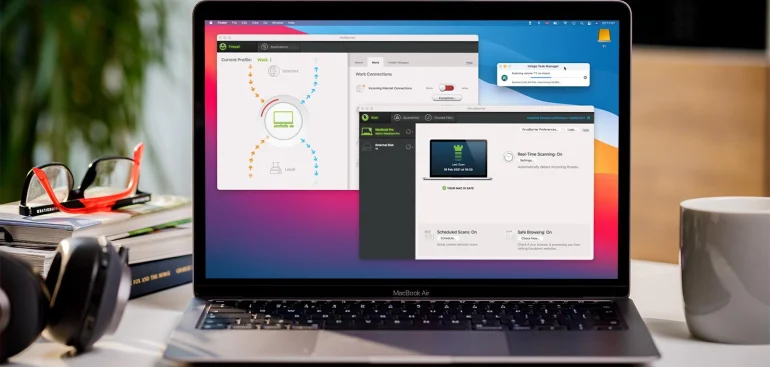
Nowadays, many people think computers can never get infected with viruses, which as Mac. But the truth is that in 2025, even devices like Apple are facing security threats like adware and phishing attacks. So, our focus is on keeping our devices secure. MacOS has many security tools built in, like Gatekeeper and XProtect, etc. But even these are not sufficient to detect every new hidden virus in today’s time, and cannot do it even effectively. So now we need a reliable virus scanner that can help secure our devices and protect user data from every virus. In today’s article, I’ve brought you some of the most popular virus scanners for Mac and their features.
Features to Look For in a Good Virus Scanner:
Real-Time Protection:
Do you know what is the meaning of real-time protection means? Let me tell you, it means that as soon as any threat, virus, or malware file comes into your Mac system, it immediately detects it and blocks it. It is very fast and secure for your device.
This is a very protected and important feature that makes your device very fast and secure. Its biggest advantage is that it keeps your Mac’s files, emails, and web browsing safe and secure. It gives you 24/7 protection.
Easy Interface:
Guys, this is its important feature which is very beneficial for you. It makes the antivirus software simple and easy. You do not need a very high qualification to use it. It has a very simple interface; anyone can use it easily.
In this you only have to install the antivirus, and its settings are also simple, which you can do easily. You will not get any confusing options in this; you will get everything as per your comfort.
Web Protection:
Friends, this is an important feature that protects your Mac from threats that exist on the Internet. For example, if you visit any website, this protection detects any infected downloads and antivirus software malicious links and blocks them.
This is really a wonderful feature for the protection of your Mac device. Through this, you can keep your online shopping and personal information safe. So, don’t think too much, these are all the features of the best virus scanner for Mac, which is very useful.
Best Virus Scanners for Mac in 2025:
Bitdefender Antivirus:
This is a highly trusted and very best antivirus software for Mac that provides strong protection against malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. It comes with so many amazing features that it can prove to be the best option for you. It provides real-time protection and a scanning feature that constantly monitors your Mac so that any threat can be detected immediately and blocked quickly.
Talking about its design, it is lightweight and does its work very fast without affecting the speed of the Mac at all.
Norton 360 Deluxe:
This is a very powerful and best antivirus. You get many features in it which are perfect for your device and help keep it safe. Its biggest advantage is that it will not only protect your Mac, but it is also helpful in keeping your iPhone and iPad devices safe. This Norton 360 Deluxe is very amazing.
Now, without any delay, choose it today and keep your devices safe. As I told you that their interface is very simple, which does not create any issue for you in using it.
Conclusion:
So, as we all know well that the internet is becoming more important for us day by day. But we cannot deny the fact that new threats are increasing here every day. Now, even famous brands like Macs are not secure. These are secure to some extent, but if you say that these are completely virus-proof, then you are thinking something wrong. In this way, the best virus scanner for Mac becomes very important. If you want to keep your device safe from viruses or threats. It is a great option for your overall protection. So, without further delay, use it today and stay safe from future viruses and threats.