Today’s time is the time of technology. In today’s time, most of the work is done by data. Whatever you do today, data is being used in it. How to handle it, how will all this work be done? To make this work easy, we do it by using cloud computing. Cloud computing has changed the way we use technology. In this blog, we will know about cloud computing and its effective use, how it works?
1. Public Cloud:
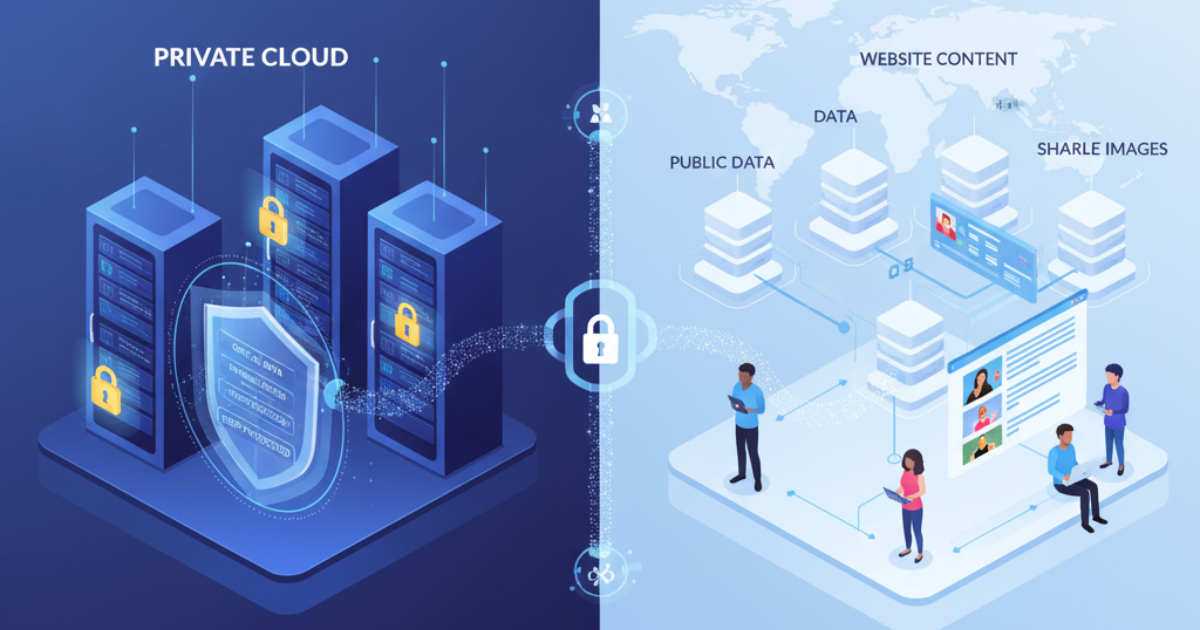
Public cloud is a type of cloud computing that is most commonly used. In this model, services and data are provided via a third-party website via the internet. Examples include platforms like Google Cloud, Amazon, Microsoft Azure, etc. In public cloud, you pay as much as you want; nothing extra is charged. There’s no need to invest in expensive infrastructure. This is mostly used in startups.
2. Private Cloud
Private cloud is another type of cloud computing. It is more secure than public cloud. It is managed by a third party, but it is used only for business. Private cloud is managed by large companies and government agencies, so there is no question of data leakage.
3. Hybrid Cloud
This is a different approach to cloud computing that uses both private and public clouds. It stores all sensitive data and is secure and untouchable. It allows you to store your private data, while in the public cloud, users share whatever is shareable.
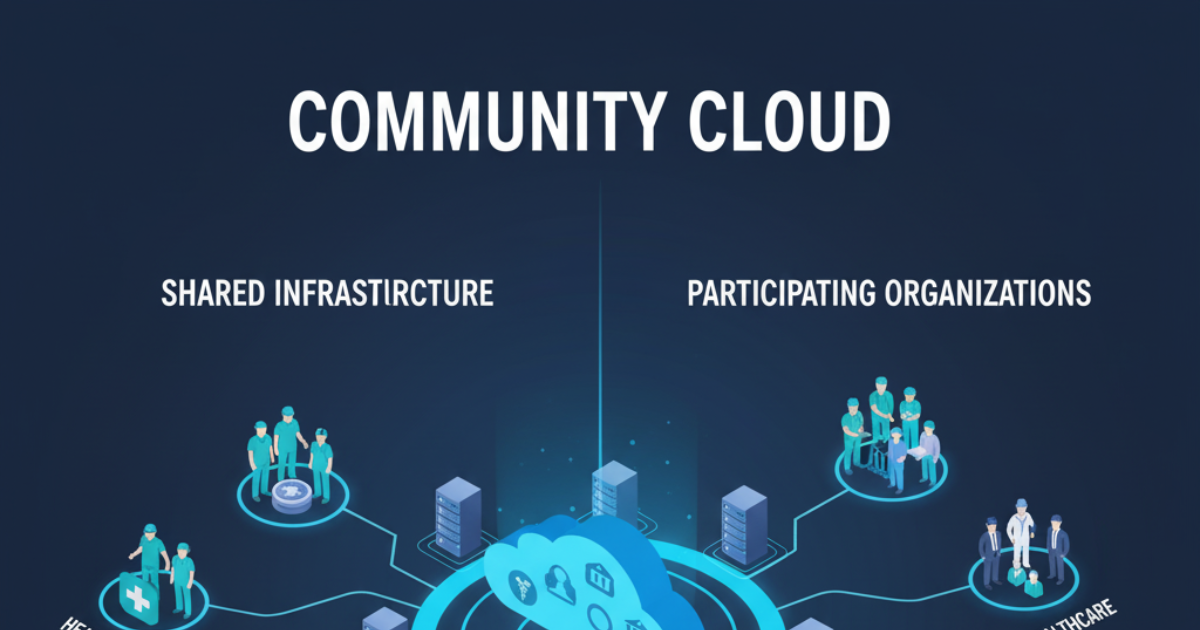
4. Community Cloud
This is also a type of cloud where many organizations work together. These include healthcare, research groups, government agencies, and many other agencies. They are used by many agencies for public welfare purposes.
Conclusion:
In today’s digital age, where everything is happening digitally, whether it’s shopping or anything else, the importance of cloud computing is increasing. As you saw in the above blog, information has been provided about all types of clouds: public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and community cloud. These all describe where they are used and how the data is stored. Data management ranges from private to public.